& the posterior ankle junction
Ankle Arthroscopy & the Posterior Ankle Junction is a minimally invasive procedure that uses an arthroscope and camera to diagnose and treat ankle joint problems. Surgeons create 2 to 3 small incisions to access the ankle’s compartments, allowing for a detailed examination and targeted treatment. The procedure uses continuous saline irrigation to improve visibility, much like arthroscopy for other joints such as the knee or shoulder. In certain cases, an articulation distraction system may be utilized to enhance intra-articular access for more effective treatment.
Ankle Arthroscopy :
Q & A
What actions can be taken with this method?
This method allows for washing the joint cavity, removing debris and osteolytic enzymes, eliminating foreign bodies, smoothing chondral lesions, resecting osteophytes, treating fracture sequelae, addressing inflammatory tissue and obstructions, releasing adhesions, and managing capsular retraction. In the hands of experts, it can also involve performing an arthrodesis with percutaneous fixation, such as screwing.
What is a posterior conflict?
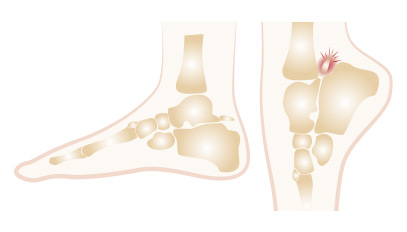
The posterior ankle junction is the anatomical region located at the back of the ankle. It consists of several bones: the tibia at the top, the talus in the middle, and the calcaneus at the bottom. Sometimes, a bone called the trigone is located at the tail of the slope behind, which is not fused with the slope. This bone can become painful due to certain traumas or repeated movements, particularly in athletes or dancers, especially those who dance on their toes frequently.
Ankle Arthroscopy: Terminology
Ankylosis: This condition occurs when a joint fuses spontaneously. It causes stiffness and restricts movement.
Arthoria: This term refers to a surgical procedure that limits a joint’s movement. For example, the Grice operation affects the articulation beneath the talus.
Arthodesis: This procedure blocks a joint surgically. It fuses two bones and prevents movement to relieve pain.
Articulated shoe: This shoe is lightweight, strong, and adjustable. It fastens with Velcro for comfort and mobility.
Chopart calcaneus: This triangle forms from the tendon, the upper edge of the calcaneus, and the posterior aspect of the tibia.
Foreign bodies: These fragments come from detached osteochondritis or bone pieces from tibial pylon fractures or slope injuries. They act as intra-articular foreign bodies.
Lambrinudi: This term refers to arthrodesis of the tibiotalar joint and the Chopart articulation.
Joint washing: Surgeons perform this procedure during arthroscopy. They use physiological serum to clean and irrigate the joint.
Mosaic: This technique involves taking cartilage grafts from a healthy joint. Surgeons implant them into areas with cartilage loss, forming a mosaic pattern.
Haglund’s disease: A bony prominence forms on the tuberosity of the calcaneus. It causes pain due to friction from the shoe’s edge. Treatment may include adjusting footwear, local care, or surgery if conservative methods fail.
Osteochondritis: Lesions affect both bone and cartilage. They isolate fragments that detach and act as intra-articular foreign bodies, causing pain or episodes of “blocking.”
Dwyer’s osteotomy: Surgeons perform this extra-articular surgical procedure. They cut the calcaneus to correct an axial deviation.
Navicular bone accessory (supernumerary scaphoid): This is an unfused bone in the tarsal scaphoid, typically located on the medial side.
Physiological Valgus: This describes the natural outward orientation of the rear foot. It usually occurs at an angle of 5 to 7°.
Varus hindfoot: This condition occurs when the hindfoot loses its lateral orientation. It tilts inward toward the medial side.
