or prominent heel
What is Haglund’s disease or prominent heel?
It is a deformation of the heel bone: the calcaneus above and outside. Occurred as a result of heel friction against a rigid stiffening boot or, more simply, by friction of the heel against the upper edge of the rear part of the boot.
It is a posterior tatalgia that sounds on the Achilles tendon and forms an inflammatory bursitis that causes heel pain that can become disabling. It is more frequent in humans, young 30-45 years: Clinically: it is a pain associated with a gene in the footwear, which can lead to lameness and difficulty in the practice of sport. In advanced forms, we may witness a redness with the formation of a serous purse which may contain pus.
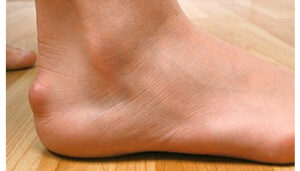
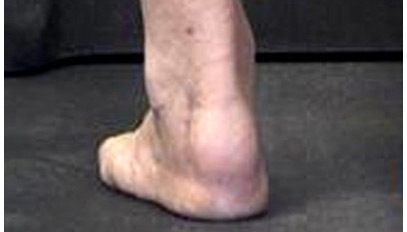
Haglund’s disease:
Q & A
Are there any causes for this?
The footwear and the footwear, in particular rigid edge and badly adapted safety shoes.
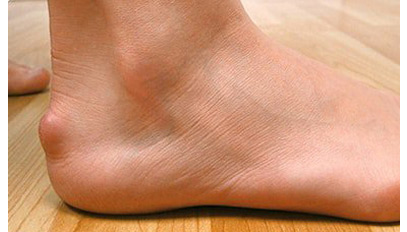
How to treat this disease?
In the absence of pain, therapeutic abstention and surveillance. The modification of the type of shoe is the basis of the whole treatment, soft shoe with stiffer buttress, shoe rising;
- Medical: NSAIDs, Analgesics, Insoles, Corticoid infiltrations, Massage: Stretching;
- Surgical: if conservative treatment fails;
- A closed hearth, percutaneous and / or arthroscopic: consists of planing the bone protrusion;
- Dwyer osteotomy, which requires fixation by osteosynthesis, screwing or staples after resection of a bone prism.

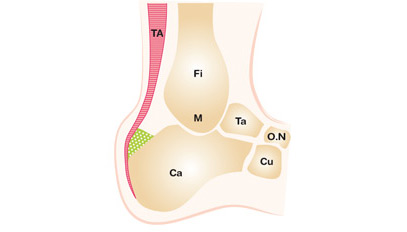
Description of Dwyer’s Osteotomy
Dotted: the exostose to be resected; Osteotomy of subtraction of the Calcaneus known as Dwyer.
- FI : Fibula
- AT : Achilles tendon
- M : malleolus
- Ca : calcaneus
- Ta : Talus
- N.B. : Navicular bone
- Cu : Cuboid
Complications ?
Healing disorder, sensitivity disorders and risk of recurrence.
Any rest or stop of normal activities?
Six weeks, including 3 with shoe discharge, time of healing, maximum 8 to 10 weeks with resumption of sport, at least 12 weeks after.
Haglund’s disease: Terminology
Exostosis: Bony protrusion, at a distance from the joint, its formation is related to the excess friction of the bone against a rather rigid body, the shoe for example.
Osteotomy: Section of the bone in order to straighten an axis, is done with the surgical saw, or by weakening the bone by perforations all around the bone, in postage stamp making the correction possible by a bone Simple manual tensioning effort. It is a kind of “fracture” for therapeutic purpose, Dwyer described a prismatic osteotomy.
Inflammatory bursitis: serous, reddish, sometimes liquid fluid formation indicative of mechanical friction.
Ulcerative bursitis: inflammatory bursitis with thinned skin that can ulcerate.
Shoe heel: part that covers the hindfoot, and is in contact with the heel.
