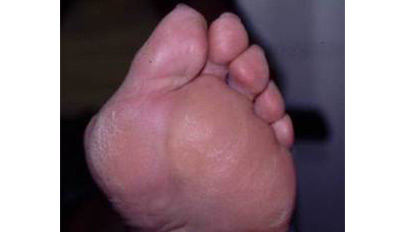
pathology frequent recurrent
The skin is a “tissue” like any other, it envelops the body, it is of different thickness according to the localization, very thin in the eyelids (a few mm), thicker in the trunk and hips, it reaches 8 to 10 mm at the level of the sole of the foot.
Mobile on the back of the hand and at the level of the eyelids, it is fixed and “adherent” at the level of the plant. In continuous renewal, the skin’s so-called epidermis is made up of layers of cells, each layer is made up of cells spread out, next to each other and affixed like tiles whose major axis is parallel to the area ; These cells become flattened, and as the layers rise towards the surface, they lose their thickness and eventually dry up and fall. The surface layer is called the stratum corneum. And the skin that falls is sometimes called the “horn”. (Fig. 1)

The “biomechanics” of the skin
The skin is a tissue like, Its first quality is elasticity, it can withstand elongations when losing weight and return to the initial shape if the individual loses weight. In some cases of deformity, this elasticity is exceeded, and the skin can “crack” giving “stretch marks”. On the moving regions, facing the joints of the fingers or the toes, the elasticity is even greater. The adhesion to the deep tissues is another mechanical quality, light on the back of the hand, it is very adherent to the level of the sole of the foot. The specificity is that it is the envelope of the body, the whole body (except in regions where there are orifices or the skin is continuous by mucous membranes) and therefore it has several roles:
- Body protection
- Participates in “thermo regulation”
Mechanical Reason
When the skin is under repeated pressures, it suffers and always reacts in the same way. If the friction seat on a moving area, such as facing a joint, redness forms in front of the joint. Due to the movements, a detachment takes place, a “pocket” is formed which eventually contains liquid, and then constitutes a “bursitis”. Sometimes, especially if there is no mobility in relation to the joint, the friction creates more layers of cells, and the skin responds to the mechanical stress by increasing the number of layers of cells. It ends up forming thick zones, called zones of hyperkeratosis.
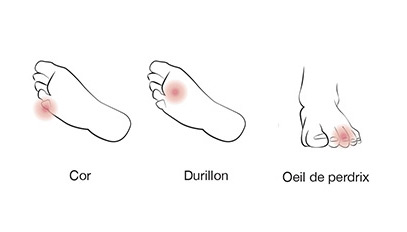
Hyperkeratosis and Keratoma
Hyperkeratosis
Etymologically it is an excess of keratin. It is a histological reaction to a mechanical constraint. It is an appellation that is due to excessive keratosis, keratin being the substance generated by the skin itself, the inert “horn” which is none other than the degenerative tissue of the death of the superficial cells of the layers Of the skin, “hyperkeratosis” is the translation of the skin’s nourishment, that is, the skin thickens to become more “resistant”.
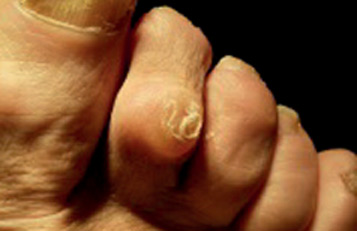
The Keratome
As a topographic term,the “keratome” is an area of skin suffering that is to say thickening of the skin to make it more “resistant”. It is a hyperkeratosis, the histological aspect of which is organized, hardened and perforated in the middle, and can become superinfect, and it is this hard, rigid, more or less infected aspect which is at the base of pain.
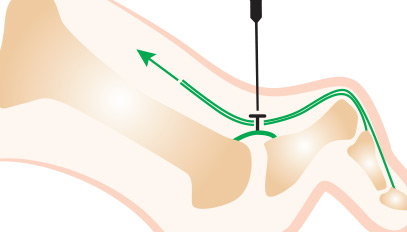
Keratoma: Treatment
As a topographic term,the “keratome” is an area of skin suffering that is to say thickening of the skin to make it more “resistant”. It is a hyperkeratosis, the histological aspect of which is organized, hardened and perforated in the middle, and can become superinfect, and it is this hard, rigid, more or less infected aspect which is at the base of pain.
The treatment of hyperkeratosis and / or keratosis which are cutaneous lesions, whatever its topography, obeys the same principles (see Gri es des toes):
The conservative medical treatment which is first of all a symptomatic treatment is followed in the event of failure or recurrence, of a radical, etiological treatment, and which is most often surgical.
The Conservative Medical Treatment is essentially symptomatic, it is constituted by:
- A comfortable warmth
- Local skin care: creams, ointments, solutions
- Pedicure
- The foot orthosis
Treatment of the cause or “etiologic” is most often surgical and is limited to solving the mechanical problem which in the majority of cases is percutaneous or minimally invasive.
When medical treatment has failed or when the lesion recurs and becomes chronic, or when the skin lesion associates with an “irreducible” deformation. It consists in correcting the deformation or sometimes only reducing the irreducible appearance by making the toe moveable, and the possibility in the boot to avoid friction of the boot. It associates, on the card, one or more of the following acts:
01
Tenotomy
of the toe extensor when it is retracted. Done intra-synovially with a “beaver” blade, it is performed percutaneously. It can involve the flexor tendons: Short Flexor (SF) and Long Flexor (LF), also done with a “beaver” blade and does not require suturing. It is indicated for toe clawing or “clinodactyly.”
02
Tendon elongation
By percutaneous or open surgery, especially for large tendons, a “Z” lengthening with fine non-resorbable sutures is indicated. This is the case for the extensor hallucis longus.
03
Capsulotomy
This involves the sectioning of the joint capsule. For example, in a claw toe, capsulotomy of the interphalangeal joint is sometimes necessary, and it is performed via the plantar approach.
04
Osteotomy
This involves cutting the bone for axial correction, which can be done in different ways: with an oscillating saw, a simple low-diameter drill bit, or a Shannon burr, which creates holes in the bone and weakens it. This method involves making a series of holes in the bone (creating a “postage stamp” appearance), leaving a cleverly planned bony bridge that can be completed with a manual maneuver.
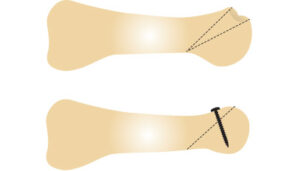
Osteotomy: Reinforcing the osteotomy with a screw or without osteosynthesis, removing a wedge or sometimes without removing one, simply by sliding the head.
05
Arthroplasty
It consists of removing one of the two joint surfaces of a toe joint, such as the interphalangeal joint, to correct the alignment and align the toe, as in the case of claw toe.
06
Arthrodesis
It consists of removing both joint surfaces of a toe joint, such as the interphalangeal joint, to correct the alignment and align the toe (as in the case of claw toe), by immobilizing the joint using a temporary pin or by placing an implant. The disadvantage is that it permanently eliminates joint mobility, making it a therapeutic choice.
The eye of partridge and the “Plantar Wart”
The eye of partridge
As a topographic term, the “partridge eye” is an area of cutaneous suffering sitting on the medial or lateral face of a toe. In fact, it is more or less the result Ischemia of a friction between two toes which have all two (or for one of them) an irreducible deformation, this is a circular thinning of the skin with a progressive disappearance of the capillary vascularization in the zone Of friction, it becomes painful when it is complicated by an infection which may reach the bone, or of a mycotic superinfection, if the medium is moist. A radiological assessment and a biological examination must be able to eliminate a dangerous complication: osteitis.
When the deformity is or becomes irreducible, and the friction is excessive, a skin reaction takes place with initially hyperkeratosis, which will be followed by a new stage, if the friction persists and worsens, a “vasoconstriction Central capillary “which consists of a central thinning and a lesion with opening and often superinfection, which is colored like the keratosis of a dark point which gives the image of an” eye “.
Treatment is medical first, it consists of local pedicure care, a more comfortable footing, in this broader sense, a mobilization of the toes disfigured by the deformation, the wearing of an orthoplasty, the night at least or the Installation of a “foam” separator or silicone fabric which can reduce friction, and at the beginning.
Surgical treatment is the solution when medical treatment fails. It concurs in a surgical correction of the deformation. This is the only way to reduce the risk of relapse.
Simple excision leads to a loss of substance: PDS (small but real) which must be supplemented by a such as a skin slide. The risk of recidivism is great if the irreducible aspect is not treated. The aim of the operative act is the suppression of the friction, by the suppression of the deformation, or its irreducible character.
The treatment of the cause, that is to say by the correction of the deformation, reduces the possibilities of recurrence. Percutaneous surgery is very useful in this kind of pathology, it has undeniable advantages over traditional methods more invasive.
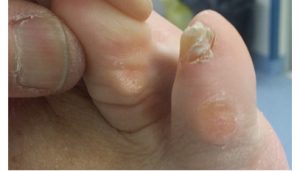
The “Plantar Wart”
The “wart” is a cutaneous lesion complicated by Infection, often occurring in an area of hyper-support, it is an area where repeated friction, a zone of hyperkeratosis, occurs. Moisture, friction zone and heat are favorable causes.
Treatment is medical in the majority of cases, combined with hygiene measures to avoid reinsertion. Various techniques are proposed, exfoliating products, cryotherapy, Liquid Nitrogen or Laser destruction. But this is not known in some cases. Sometimes, there are several warts juxtaposed, which constitutes a “warty” plaque.
Surgical excision is the last resort. The procedure consists in a pure and simple resection without skin closure to allow to heal according to a “directed healing” which can last 2 to 8 weeks depending on the size of the lesion.
In other cases, a covering plasty which consists of a dissection step by step to play the elasticity of the skin to make it slide.